Forex trading is constantly growing in popularity. New Forex brokerages are opening at an extremely high rate. Many people who are used to working 9-5 jobs are now leaving their jobs and starting to trade Forex. There are many explanations for the growth of the Forex market, some of the obvious ones being its size, its simplicity, and its potential for profit.
When one thinks about Forex as opposed to other global markets such as the stock exchange, some very basic differences should come to mind. These include higher liquidity, more volatility, greater leverage, as well as lower trading commissions and costs. We have already discussed the liquidity, volatility, and leverage offered in the world of Forex, so now we will learn a little bit more about the trading costs and commissions as compared to other global markets.
Top Regulated Brokers
he Stock Market
Let us take the stock market for example. When one trades stocks, which by the way, is a very common occurrence for Forex traders (a lot of people fail at stock trading and then turn to Forex, and rightfully so), the standard way trades are conducted is with the trader being charged commission on both sides of the trade. What does that mean? When you trade stocks, you are generally doing it in cooperation with a broker, and that broker charges you a fixed dollar amount per trade, a dollar amount per share, or a scaled commission based on the size of your trade. This commission is applied when you buy a stock, AS WELL as when you sell it.
Forex Trading
Now let's talk about Forex trading and how Forex works. The vast majority of Forex brokers will advertise in very big letters somewhere on their site that they do NOT charge commission. With the exception of a few brokers, the Forex market lets traders open and close positions with no commission at all.
How Do Forex Brokers Make Money?
So, it costs you nothing to trade. This of course begs the obvious question: “How do Forex brokers make money?” Here is where it gets tricky. It is true that there are brokerages who charge no commissions in Forex trading, but the brokers are also not trading for you out of the goodness of their hearts. You can be sure that they come out on top, and in a big way. They charge you what's referred to as “Forex spreads”. The brokerages with lower spreads, often do charge commissions in addition to the spread. It is extremely important to understand all the costs related to your trades before you make major decisions.
Before we understand what Forex spreads are and how they are calculated, it is important to understand one main principle about how the Forex market works. It is all based on supply and demand, just like any other market. If there is a higher demand for dollars, the value of the dollar will go up vs other currencies. This is precisely how Forex spreads are defined and calculated.
Forex Spreads
A Forex spread is the difference in price between what a Forex broker will buy the currency from you for (the “ask price” and the price at which they will sell it (the “bid price”). So, for example, if you are opening a position in which the base currency is U.S. dollars, and since there is no shortage in demand for dollars, the Forex spread on this transaction will almost always be smaller than a spread on a less common currency. Why?
This is again because of supply and demand. The broker will have no problem whatsoever selling off the dollars they just bought, so they do not need to charge you, the trader, a higher spread. Whereas, if the position's base currency was the Vietnamese Dong (yes, that is the name of the currency in Vietnam), the spreads will typically be higher. It means the broker is taking a bigger risk and as a result can charge more for that risk. Because of this, it is recommended for the individual trader to avoid buying or selling currencies with lower demand. It will cost much more because of the higher spread.
As a rule of thumb, the bigger the currency, the lower the spread. This is why the lowest spread you will get will be in a currency pair such as the EUR/USD, while trading an exotic cross such as the Mexican Peso against the Hungarian Forint will have a huge spread.
If a broker were to buy and sell currencies with no change in the exchange rate, the trader would lose money because the sell (ask) price is always higher than the buy (bid) price, enabling the broker to always make some money on the transaction. On a small scale you see this if you exchange money at a bank when you travel. They will always offer more when they buy your dollars then when they sell them back to you.
Another characteristic Forex brokers consider when calculating spread costs and associated calculations is the type of account in which you are trading. Mini accounts are typically associated with higher spreads. This is of course because the broker needs to compensate the relatively low amount of capital being traded with a higher spread, so as to make their profit.
A mini account might be trading in the tens of thousands of currency units, whereas most Forex trades are closer to a million units. This means that if the spread is .0004 or 4 pips it can cost the average Forex trader 400 GBP or USD or whatever currency they are trading in.
Now, that we established that as attractive as Forex trading is, it is not completely cost free, let's understand the difference between Forex spreads and stock market commissions. The primary difference is that in Forex, you are generally only charged a spread on one side of the transaction, the “buy” side. When you buy currency that is when brokers generally make their profit by charging you a spread.
It is extremely crucial that traders understand how significant the spread is when choosing a broker. The difference one Forex pip can make in a broker's spread might be the difference between a successful Forex trader and a complete Forex failure. A pip is defined as the fourth digit after the decimal.
How Do Forex Spreads Work?
Just to summarize, let's take a look at a concrete example of a spread and understand how it works exactly, meaning, how is the spread in Forex trading measured? Let's say as a sample calculation, we had a EUR/USD bid price of 1.13404 (that is the price at which the broker is willing to BUY the EUR) and an ask of 1.13398 (the price at which the broker is willing to SELL the EUR). In this case, the spread is equal to 0.6 pips, and that money goes straight into the broker's pockets.
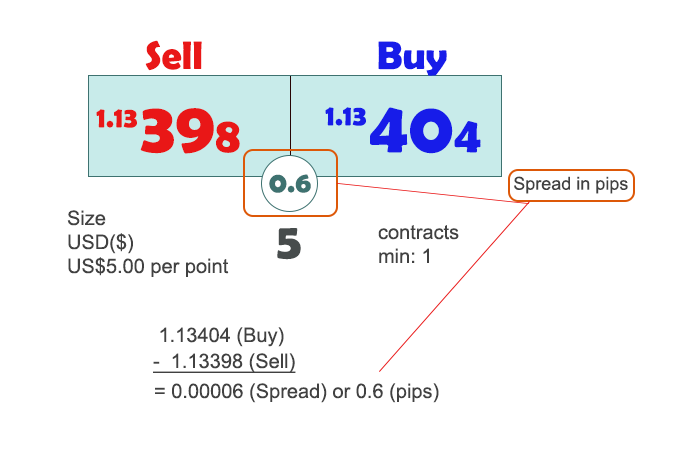
There are charts readily available on the internet that enable you to see Forex spread comparison. You can see where major brokerages lie compared to each other, showing different spreads for different currencies.
The spread is just a number but to see how much it would actually cost a trader you need to figure out the mathematics involved. That means to see what it costs, you have to multiply the spread in pips by the pip cost per 10K lot of currency, giving you the spread cost per 10K. Obviously, your cost goes up by the number of currency lots you are trading.

Even fixed spreads change periodically so it is very important to stay on top of what your brokerage is charging. Many market makers charge a smaller spread during more common trading hours to encourage people to do more trading when there is more demand.
There is so much more to be said about Forex trading spreads, such as whether a broker offers fixed or variable spreads and which is better for the trader. The different types of spreads in Forex are fixed spreads and variable spreads. Fixed spreads, as the name suggests, remain the same and never change, while variable spreads fluctuate as market conditions change minute by minute. Fixed spreads are almost always higher than variable spreads, because they include some form of insurance. The advantages of fixed spreads are that they are predictable and may be lower than a floating spread sometimes. The disadvantage of fixed spreads is that they are usually higher than floating spreads and so cost the trader more. The advantage of floating spreads is that they are usually lower than fixed spreads so cost the trader less. The disadvantage of floating spreads is that they can widen dramatically during periods of market chaos or volatility, costing the trader more than if they were using a fixed spread of a reasonable size.
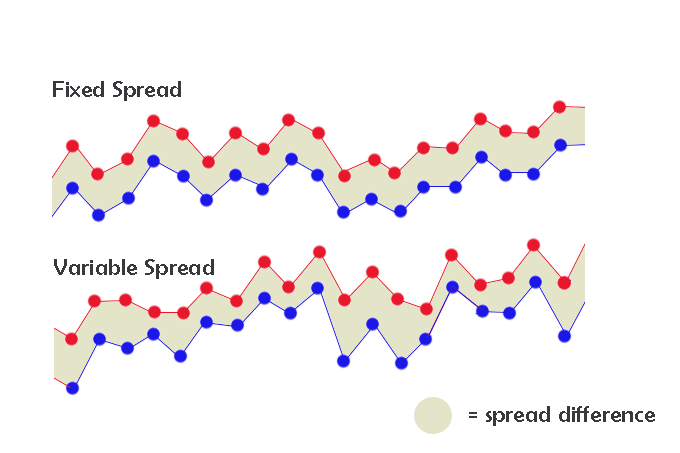
Be aware that often, brokers who offer fixed spreads restrict trades during news announcements when the Forex market is particularly volatile. Thus, the insurance really doesn’t help you. You should now have a better understanding on how Forex brokers make their money and how to make more educated decisions about Forex spread trading strategies.
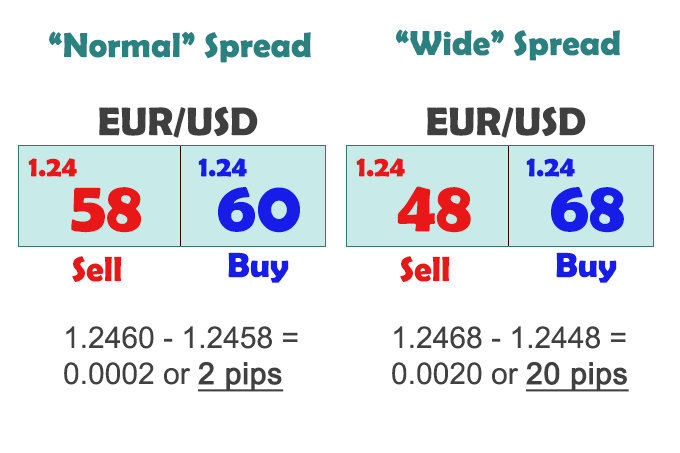
Understanding a High Spread and a Low Spread
A “high” spread is one where the difference between the bid and ask prices at the moment you make a trade is relatively high. This is bad, because you start the trade in a somewhat bigger loss. Remember, you always start a trade at a small loss unless you are lucky enough to have entered a trade with an ECN broker during a very rare moment when the spread is “inverted”. An inverted spread happens when the bid price is momentarily less than the ask price, and it only happens at an ECN broker.
A “low” spread is one where the difference between the bid and ask prices at the moment you make a trade is relatively low.
For example, let’s say that you see that your broker is quoting EUR/USD at a bid price of 1.1001 and at an ask price of 1.1000. The bid price is the price at which you can enter a long trade or exit a short trade. The ask price is the price at which you can enter a short trade or exit a long trade. So, if you enter a long trade at that moment, your trade will begin immediately at a floating loss of 1 pip, because you entered that trade at 1.1001 and would theoretically exit it at 1.1000: a difference of minus 1 pip. Note that if the spread widened, with the ask price going down by say another 2 pips to 1.0998, you would be in a floating loss of 3 pips; if the spread narrowed instead, with the asking price going up by half a pip from 1.1000 to 1.10005, you would be in a floating loss of half a pip.
Entering trades when the spread – the bid/ask differential – is relatively low means you begin a trade with a slightly better overall position. This is why it pays to at least quickly mentally calculate the “cost” of the spread before entering a trade.
What Affects the Spread in Forex Trading?
It is easy to understand that in a natural Forex market offered by a broker with variable spreads, the spread as the difference between the bid and ask prices will fluctuate from moment to moment. What is less easy to understand is why these fluctuations happen. The simple rule is that the more active buyers and sellers there are in a market, the smaller the spreads will be. During moments of great fear or uncertainty, market participants will withdraw, leading to a drop in liquidity and sharp and volatile widening of the spread.
How to Manage and Minimize the Spread?
Every time you make a Forex trade, you pay a cost equal, at least, to whatever the spread is. This means the spread on your trade is the cost of doing business. In business, it is always a good idea to keep your costs down if you can, so how can you keep trading but pay less in spreads? There are several answers. Firstly, it is almost always a good idea to use variable spreads. Secondly, you should try to use a Forex / CFD broker which charges relatively low spreads, and usually the more money you deposit, the better a deal on spreads you will buy yourself, which means that depositing more than one thousand dollars if you can afford it should help you to “afford” better spreads. Thirdly, if you have a sizable deposit, using an ECN broker can help reduce the spreads you will pay. Finally, taking trades during times of peak liquidity in the instrument you are trading, should ensure that your floating or “variable” spread will be minimized, as spreads tend to be lowest during times of peak liquidity. This time of peak liquidity is usually found in most Forex currency pairs during the overlap of London and New York business hours, which corresponds to between approximately 1pm to 5pm London time. As London and New York are the two major global hubs for Forex trading, it makes sense that the time of great liquidity will be when both centers are online. For some currency pairs, most notable Asian Forex crosses such as the AUD/JPY, the Tokyo session can also be very liquid – as a rule, if the home country of a currency is open for business, there should be liquidity in that currency.
Be sure to avoid trading during periods leading up to or immediately following major relevant news or economic data releases, as spreads tend to widen dramatically at these times.
How Forex Brokers Profit from Spreads
Don’t think, though, that Forex brokers make their money by charging spreads and commissions. The clear majority of retail Forex brokers make their money by taking the other side of their client’s trades, most of whom lose their money, which goes straight into the brokers’ pockets. It is important not to be naive about this, but you don’t have to believe that your broker is out to get you or cheat you either. How does this work? Well, imagine a Forex broker that does nothing else but give you prices at which to trade after taking your deposit. If you, and the clear majority of their other clients, trade badly and lose all your money without ever withdrawing any profit, then they will make much bigger profits by keeping your deposits than they ever will from any spreads and commissions that you are charged. Of course, higher spreads and commissions help a broker to make more money more quickly, but if they are not putting any real transactions on in any real market – and this is the case with a huge majority of all retail Forex brokers, even the ones that claim to operate with a “no dealing desk” model – then it is not very important. The spread is far more important to you, as a trader, than it is to the broker. It is your “cost of doing business”, and the more frequently you make a trade, the more important the size of your spread becomes to your overall profitability.
